Departmental Activity
Departmental Schedule
- Mon - Tues :
10.00 am - 05.00 pm
- Wednes - Thurs :
10.00 am - 05.00 pm
- Fri :
10.00 am - 05.00 pm
- 2'nd & 4'th Sat.
Open
- Sun :
Colosed

 About Department
About Department
|
 Programme Offered
Programme Offered
About Program
Our Courses
![]() Eligibility Criteria
Eligibility Criteria
![]() Eligibility Criteria
Eligibility Criteria
 Syllabus
Syllabus
Teaching Syllabus
 Programme Outcomes
Programme Outcomes
PO-CO-PSO
| Course | Course Outcomes |
|---|---|
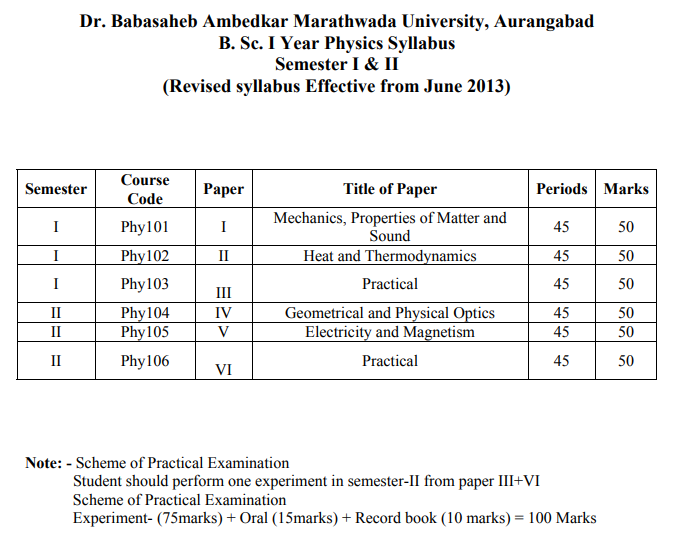
| F.Y. B. Sc. Course PHY-101: Semester I Mechanics and Properties of matter and sound Paper I Basic Outcomes of Course : | 1. Learner will understand basic theorems and concepts of basic physics. 2. To understand concept of gravitation, gravitational field, gravitational potential. 3. To understand the dynamics of different types of compound pendulum and to determine ‘g’. 4. To understand the elastic properties of matter and expression of bending beam with its application as a cantilever. 5. To understand concept of Viscosity. 6. To understand concept of fluid flow and pressure energy in fluids. 7. To determine Bernoulli’s Theorem and its applications: (i)Filter Pump (ii) law of Hydrostatic Pressure 8. To design experiment to determine coefficient of viscosity by using Poiseuillie’s equation. 9.To understand concept of surface tension and its relation with excess pressure and radius of curvature. 10. To determine the surface tension by Jaeger’s method from experiments. 11.To understand Piezo-electric effect, Magnetostriction Effect 12. To understand generation of Ultrasonic waves 13.Applications of Ultrasonic Waves: Depth of sea, Chemical Effects, Medical Applications. 14.To understand concept of sound waves. 15.Reverberation,Propogation of sound. 16.Acoustical demand of Auditorium, conditions of good acoustical designs of room. 17.Sabines law and its derivation. 18.To develop basic skills to perform experiments to understand the concept from existing theories of Basic physics. |
|
Paper V |
. To understand basic concept of vector algebra. 2. To understand Triple product of Vectors and scalars. 3. To understand Physical significance and geometrical significance of triple product. 4. Apply techniques of vector analysis, such as gradient of scalar, divergence of vector, curl of vector 5. To understand line, surface and volume integrals. 6.To understand Gauss Divergence theorem and Stoke’s Theorem. 7.To understand concept of static charges, Electric field ,flux. 8. To understand and derive Gauss law in electrostatics , its differential form. 9. To understand concept of electric dipole, potential and field due to dipole. 10.To understand concept of dielectrics, relation between D,E,P. 11.To understand the concept of magnetism and and magnetic properties of materials. 12. To understand concept of magnetic induction. Biot - Savert Law, Ampere Law. Construction and working of Moving coil Galvanometer 13.To determine Time constant of L-R and C-R circuit and its physical significances. Growth and decay of currents in various circuits. |
| PHY 103 and PHY106 : Semester III+IV Practical Physics Paper III and Paper VI |
M.I. of a rectangular lamina torsional pendulum. 2.η by Maxwell’s Needle oscillation. 3. Determination of acceleration due to gravity by Kater’s reversible pendulum. 4. Determination of Y using flat spiral spring. 5. Determination of ηby using flat spiral spring. 6. To determine Y of rectangular beam by method of bending. 7. To determine Y by vibrational cantilever. 8. Moment of inertia of a flywheel. 9. Determination of coefficient of viscosity of water by Poiseuille’s method. 10. To find field along the axis of a coil. 11. To determine the surface tension by Jaeger’s method. 12. Thermal conductivity by Lee’s method. 13. Study of CRO. 14. Calibration of Spectrometer. 15.Dispersive power of prism.16.I-H curve. |
| PHY 103 and PHY106 : Semester III+IV Practical Physics Paper III and Paper VI |
• To study phase diagrams and elementary idea of catalysis. • Students to learn about electro chemistry. To study EMF, pH and their applications. • Electrochemistry discussed electrical properties of ionic solutions. Different applications are there of this course. |
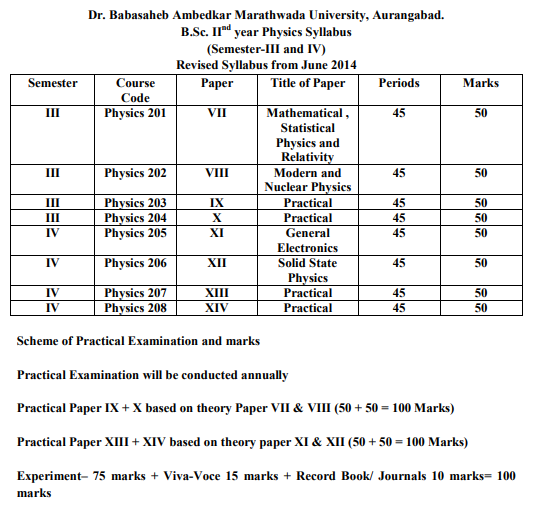
| Paper No.IX & XII Lab Course |
• To enable the students to know about principles and applications of Analytical techniques, • Evaluation of Analytical data, Statistical texts and data, Theory of Quantitative Analysis, Gravimetric methods • Enable the students to estimate the binary mixtures of metallic ions by volumetric and gravimetric methods |
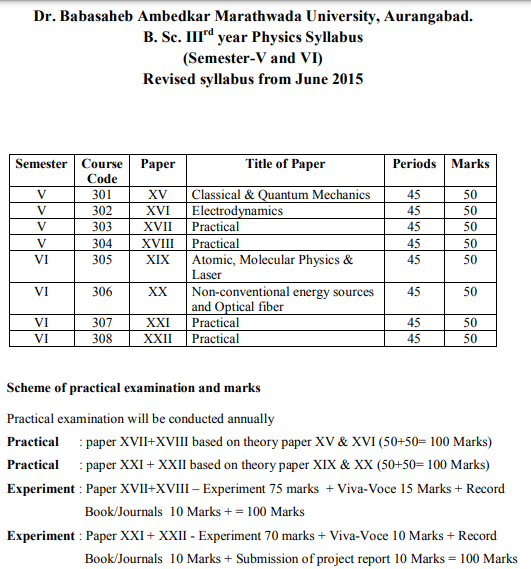
| PHY 302 :Semester V Electrodynamics Paper XVI |
. To state Gauss law and its application to obtain electric field for different cases. 2. Describe and explain the relationship between the electric field and the electrostatic potential. 3. Understand the relation between Electric displacement vector D, Susceptibility, Permittivity, Dielectric constant. 4. To understand Faradays laws of EM induction . 5.To understand the concept of electromagnetic induction, self induction of solenoid, mutual induction of coaxial solenoid 6. Be able to solve relevant theoretical problem and use their conceptual understanding of the electromagnetic laws in order to qualitatively describe the behavior of the solution to the problem. 7. Understand origin of Maxwell's equations in magnetic and dielectric media 8. Write down and derive Maxwell's equations in linear, isotropic, homogeneous media 9. To derive continuity conditions on electromagnetic fields at boundaries 10. To derive electromagnetic wave solutions and propagation in conducting and other media and understand transport of energy and Poynting vector. 11. To understand Polarization of EM waves. 12. To study the interaction of electromagnetic waves with matter. 13. To Show laws of geometric optics originate with Maxwell's equations at dielectric boundaries calculate reflection and transmission coefficients for waves at dielectric boundaries. |
|
PHY 305: Paper XIX Atomic and Molecular Physics and LASERS |
Upon successful completion of this course it is intended that a student will be able to: 1.To explain Thomson atom model, Rutherford Nuclear model. 2.To explain Bohr’s atom model, Bohr’s theory of spectral lines. 3.Diagrammatic representation of Hydrogen atom spectra. 4. State and explain the key properties of vector atom model and the importance of the Pauli Exclusion Principle. 5. To explain the observed dependence of atomic spectral lines on externally applied electric and magnetic fields. 4. To state and justify the selection rules for various optical spectroscopies in terms of the symmetries of molecular vibrations. 6. List different types of atomic and molecular spectra and related instrumentation. 5. Describe theories explaining the structure of atoms and the origin of the observed spectra 6. Identify atomic effect such as space quantization and Zeeman Effect. 7.to understand molecular spectra, Rayleigh scattering. 8.To understand Raman Effect, applications of Raman Effect. 9.To understand nature of liquids, Crystal Physics, nuclear physics, Chemical effects. 10. To understand LASER, various emissions involved in lasing action, properties of LASER, pumping schemes. 11.To study types of LASERs. 12. To study application of LASERs. |
|
TYBSc PHY 307 and PHY303: Semester V + VI Practical Paper XVII and Paper XXI |
Thermal conductivity by Forbe’s method. 2.Rydberg constant. 3.B-H curve using magnetometer. 4.Determination of Debye temperature. 5.Determination of dielectric constant. 6.Resistance measurement of semiconductor. 7.I-H curve by Excel. 8.Rydberg constant using Excel. 9.Measurement of focal length of lens using laser. 10.Spectral response of photoconductor. 11.Diffraction grating using laser beam. 12.e by Millikan’s oil drop method. 13.Study of Thermo couple. 14.R.I. of optical fibre. 15. constant of B.G. by condenser method. 16.Study of absorption spectra of iodine. |
|
PHY 304 and PHY308:Semester V+VI Practical Paper XVIII and Paper XXII |
1.Divergence of Laser. 2.Determination of diameter of thin wire using laser. 3.To study interference of light using optical fibres. 4.Wavelength of He-Ne laser using grating. 5. Y by Koenig’s method. 6.Edser A pattern. 7.e/m by Thomson method. 8.Surface tension by ripples method. 9.Temperature coefficient of resistance. 10. Thickness of thin film by gravimeter/optical/electrical method. 11.temperature of sodium flame. 12.Hartmann’s dispersion formula. 13.Maxwell’s bridge. 14. Wavelength λ by grating. 15.Regulated power supply using Zener diode. 16.Bridge Rectifier. |
|
PHY 202:Semester III PaperVIII: Modern and Nuclear Physics |
1.To understand concept of Photoelectric effect. 2.To study different methods to determine photoelectrons, Lenards method to study e/m , Richardson and Compton expt. 3.To study various types of photoelectric cells and their applications. 4. To understand the Origin and nature of x-ray. 5. To study various experimental methods such as Laue, powder crystal methods. 6.To understand Bragg’s law and Bragg’s spectrophotometer. 7. Characteristic x-ray spectra, continuous X- ray spectra. 8. To understand nuclear compositions and Elementary particles, charge symmetry and independence, spin dependence of nuclear force. 9. To state Law of radioactive decay and its application. 10. To distinguish between Types of nuclear models: Single particle shell model and Liquid drop model. 11. To understand nuclear reactions and conservation laws. 12. To understand nuclear fission on the basis of liquid drop model and nuclear fusion. 13. To understand basic principles and classification of Nuclear Reactor. 14. To learn types of detectors and classification of accelerators. |
|
PHY 205:Semester IV Paper XI: General Electronics |
1.To study construction, I/O characteristics and working of various semiconductor devices such as diode, transistor, FET and MOSFET. 2.To study various biasing methods of transistor biasing, stability factors, Q point. 3. To study various amplifier circuits using transistor. 4.To study noise and feedback in amplifiers. 5.To study OPAMP, its characteristics,configuration and applications as a adder and subtractor. 6.To understand principle of oscillators and multivibrators. H parameters, various oscillator circuits. 7.To understand various types of multivibrator circuits. 8.To understand concept of Modulation and Demodulation. Types of modulations :FM, AM and PM. Advantages of modulation. |
|
PHY 203 and PHY 207 : Practical Paper IX and Paper XIII |
1. Energy band gap of semiconductor using thermistor.
2. I-V characteristics of Solar cell. 3. Calibration of bridge wire. 4. Determination of absolute capacity of condenser using B.G. 5. Full wave Rectifier with π type filter. 6. Viscosity of liquid using Searle’s Viscometer. 7. High resistance by leakage through condenser. 8. Viscosity of liquid by oscillating disc method. 9.’h’ by photocell.10. e/m by Thomson method 12. Determination of absolute value of BH and BV using earth inductor. 13. Stefan’s constant using thermo-couple. 14. Measurement of low resistance using potentiometer. 15. Determination of A.C. mains using sonometer. 16. Polarimeter. 17. Cauchy’s constant by spectrometer. |
|
PHY 204 and PHY 208 : Practical Paper X and Paper XIV |
1. Thermal conductivity of Rubber tube. 2. Study of temperature dependence of total radiation. 3. To draw the histogram of Gaussian Curve. 4. Comparison of capacities by Desauty’s method. 5. Velocity of sound using Helmoltz resonator. 6. Surface tension by Ferguson’s method. 7. R.P. of telescope. 8. Wave length by Newton’s ring. 9. Transistor characteristics in CE configuration. 10. Transistor characteristics in CB configuration. 11. Study of CE amplifier. 12. Hartley oscillator using transistor. 13. Wein bridge oscillator. 14. OPAMP as adder / subtractor. 15. JFET characteristics. 16. Self inductance by Owen’s bridge. |
 Teaching Staff
Teaching Staff
About Our Staff
|
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr.No. | Faculty Name | Qualification | Designation | View Profile |
| 1. | Mrs. Manisha Ghogare | M.Sc. | Head of the Dept | Click Here |
| 2. | Dr. Madhukar Solunke | MSc. PhD | Professor | Click Here |
 Activity
Activity
Departmental Activity
![]() Departmental Activities (2023-2024)
Departmental Activities (2023-2024)
View Activities here..

|

|
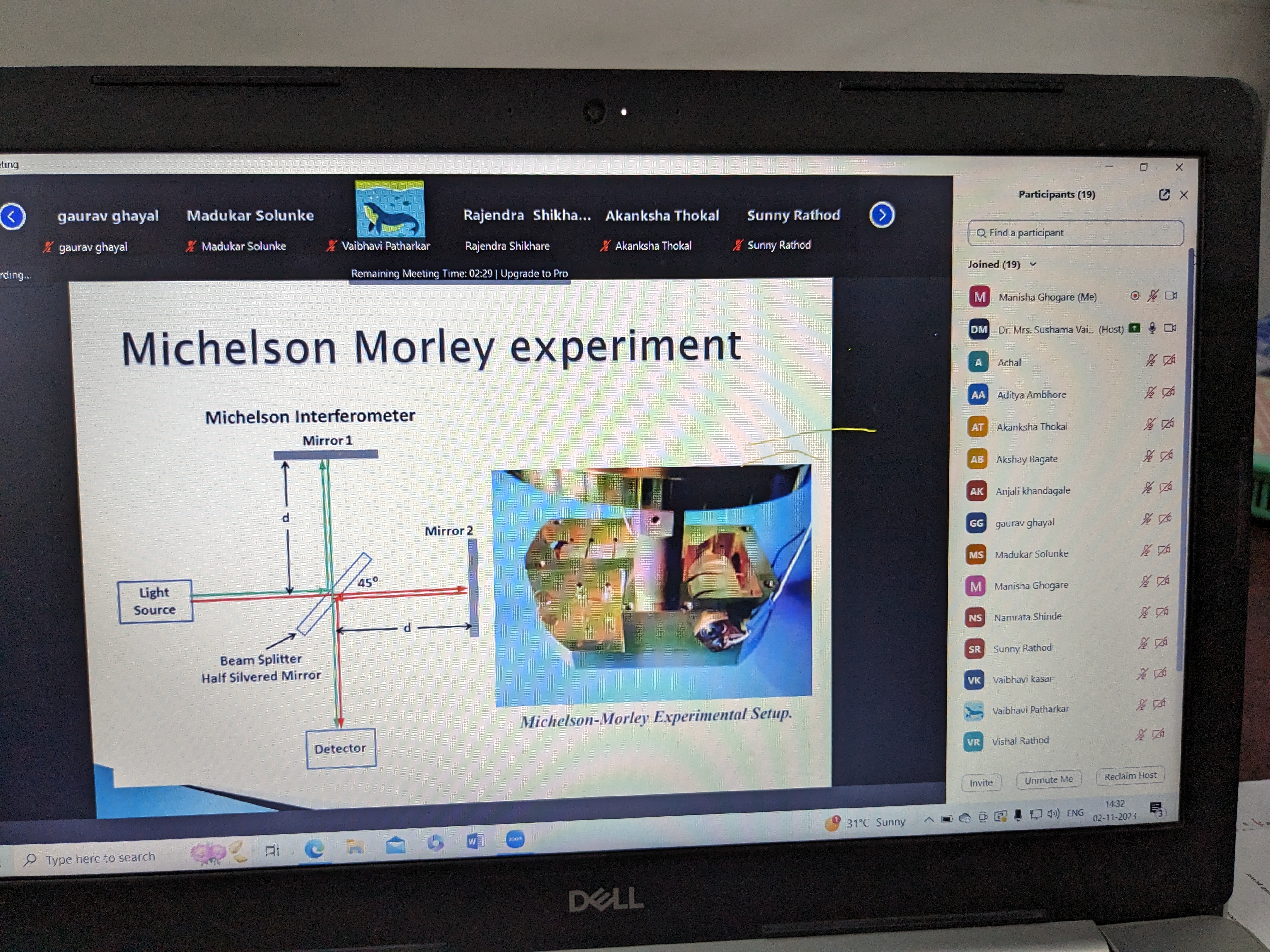
|
![]() Departmental Activities (2022-2023)
Departmental Activities (2022-2023)
View Activities here..
|
| |
![]() Departmental Activities (2021-2022)
Departmental Activities (2021-2022)
![]() Departmental Activities (2020-2021)
Departmental Activities (2020-2021)
![]() Departmental Activities (2019-2020)
Departmental Activities (2019-2020)
![]() Departmental Activities (2018-2019)
Departmental Activities (2018-2019)
1. Wall paper ‘ORBIT’ 2. Best Paper cut activity 3. Use of LMS such as Moodlecloud and Google Classroom 4. Online teaching using Zoom and Google Meet 5. Students’ Seminar 6. Quiz Competition 7. Cross word and word puzzle solving 8. Mentor-Mentee Mechanism 9. Group Discussion 10.Continuous assessment programme 11. Departmental Library 12. Whatsapp Groups of all students for communication |
View Activities here..
 Alumini
Alumini
About our alumini
| |
 |
|
| |
|
| View Profile |
|
| |
|
| View Profile |
|
| |
|
| View Profile |
|
| |
 Certificate Course
Certificate Course
About Certification Courses
Contact with Us..!
Sample Title
Sample Title
Sample Title
Sample Title
Sample Title
Sample Title

 1.Physics,Chemistry,Mathematics
1.Physics,Chemistry,Mathematics